This story was originally published by Grist and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration. Sign up for Grist’s weekly newsletter here.
Just weeks after the deadliest wildfire in modern U.S. history ripped through the coastal town of Lāhainā, Native Hawaiian taro farmers, environmentalists, and other residents of West Maui crowded into a narrow conference room in Honolulu for a state water commission hearing.
The chorus of criticism was emotional and persistent. For nearly 12 hours, scores of people urged commissioners to reinstate an official who had been key to strengthening water regulations and to resist corporate pressure to weaken those regulations. One after another, they calmly and deliberately delivered scathing criticism of a developer named Peter Martin, calling him “the face of evil in Lāhainā” and “public enemy number one.”
One person summed up the mood of the room when he said, “F— Peter Martin.”
More than 100 miles away on Maui, Martin followed parts of the hearing through a livestream on YouTube. Despite the deluge of criticism, he wasn’t upset. He wasn’t even surprised. After nearly 50 years as a developer on Maui, he’s used to public criticism.
“When you’re around a gang of people, a mob, the commissioners just listen to the mob, they don’t listen to reasoned voices,” Martin told Grist. “I’m not comparing these people to Hitler; I’m just saying Hitler got people involved by hating, hating the Jews.”

Martin, who is 76, has long been controversial. He moved to Maui from California in 1971 and got his start picking pineapples, teaching high school math, and waiting tables. Before long, he began investing in real estate. His timing was perfect: Hawaiʻi had become a state just 12 years earlier, and Maui’s housing market was booming as Americans from the mainland flocked there. By 1978, local headlines were bemoaning the high price of housing, and prices only went up from there.
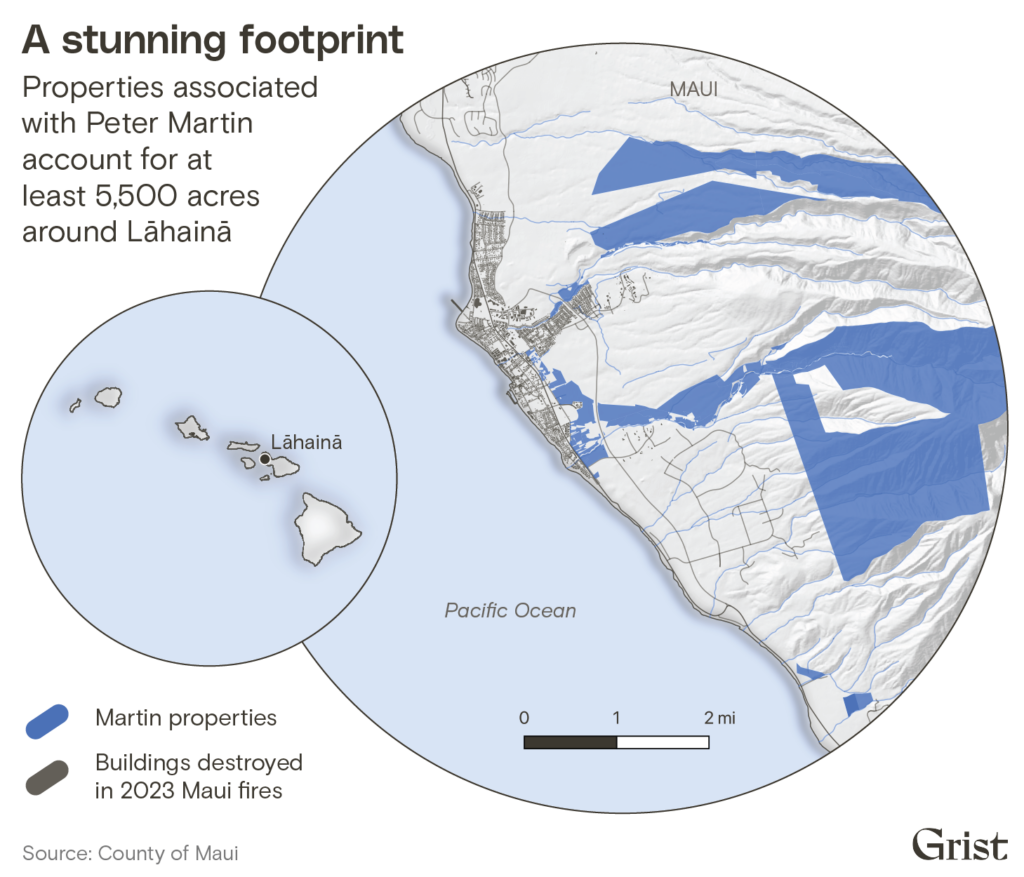
Over the last five decades, Martin has made millions of dollars off this real estate boom, building a development empire on West Maui and turning hundreds of acres of plantation land into a paradise of palatial homes and swimming pools. He owns or holds interest in nearly three dozen companies that touch almost every aspect of the homebuilding process: companies that buy vacant land, companies that submit development plans to local governments, companies that build houses, and companies that sell water to residents. His real estate brokerage helps find buyers for homes built on his land, and he’s even got a company that builds swimming pools.
Companies associated with Martin own more than 5,500 acres of land around Lāhainā, according to an analysis of county records, making him one of the area’s largest private landowners, and his web of businesses wields immense influence in West Maui, which is home to about 25,000 people. He drives his white Ford F-150 around the island with a large, black Bible on the center dashboard and peppers his conversations and emails with quotes from Scripture or libertarian economist Milton Friedman. He once served on the Maui County salary commission, where he helped determine pay for elected officials and county department heads, and he has donated $1.3 million to the Grassroot Institute of Hawaii, a libertarian think tank that has fought Native Hawaiian sovereignty. So extensive is the reach of his land empire that the command center for the response to the August wildfires is located on land owned by a company in which he has a stake.
Development on Maui, where the median home price now exceeds $1 million, often sparks controversy, and Martin is far from the only builder who has inspired opposition. But his staunch ideological commitment to free market capitalism and Christianity, coupled with his companies’ persistent pushback against water regulations intended to protect Native Hawaiian rights, has evoked particularly passionate distaste among many locals. “F— the Peter Martin types,” reads one bumper sticker spotted in Lāhainā.
And that was before the wildfire. Just two days after the outbreak of a blaze that would go on to kill 100 people, fueled in part by invasive grasses on Martin’s vacant land, an executive at one of Martin’s companies sent a letter to the state water commission. Glenn Tremble, who works for West Maui Land Company, wrote that the company’s request to fill its reservoirs on the day of the fire had been delayed by the state. He also asked the commission to loosen water regulations during the fire recovery.
“We anxiously awaited the morning knowing that we could have made more water available to [the Maui Fire Department] if our request had been immediately approved,” he wrote.
Tremble’s letter implied that a state official key to implementing local water regulations — and the first Native Hawaiian to lead the state water commission — had impeded firefighting efforts. He soon walked back the claim, but his first letter had immediate effect. The state attorney general launched an investigation into the official, the governor suspended water regulations, and the official was temporarily reassigned. Critics saw it as an attempt to capitalize on the grief of the community for profit.
It didn’t help that within weeks, when the Washington Post asked about the role the invasive grasses on Martin’s land played in the deadly wildfire, Martin said he believed the fire was the result of God’s anger over the state water restrictions.
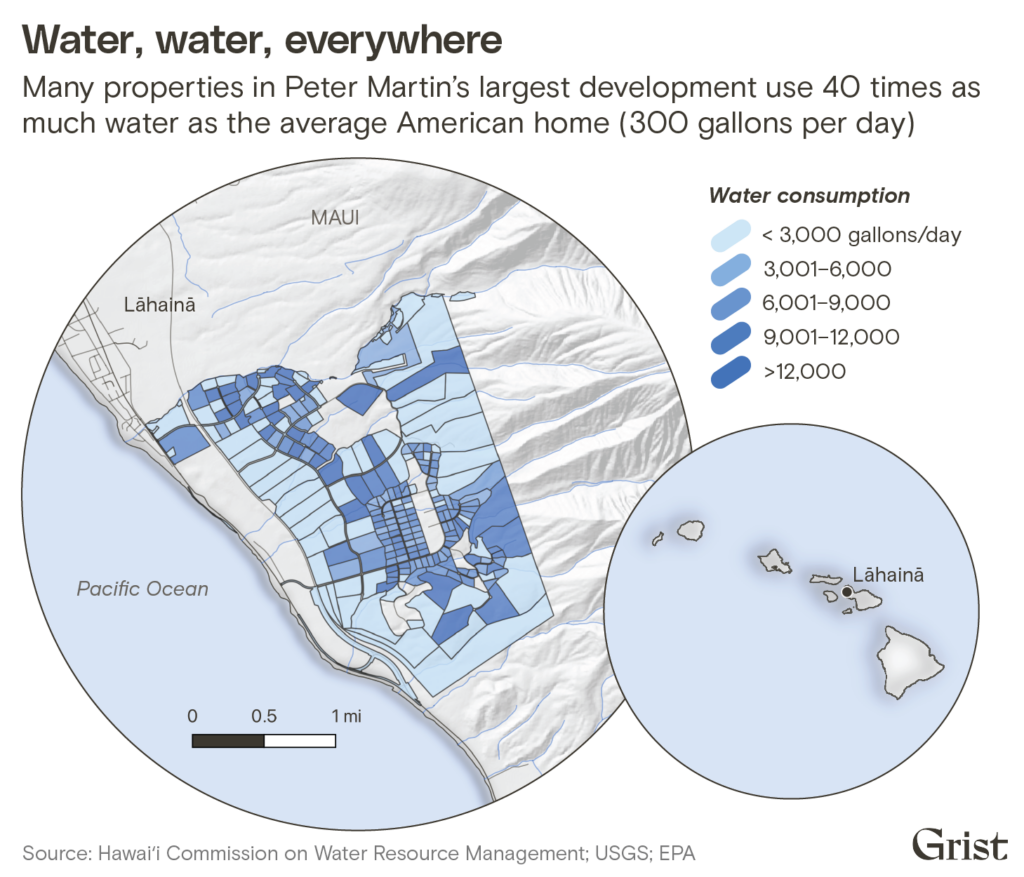
Most people in West Maui get water from the county’s public water system. But Martin-built developments such as Launiupoko, a community of a few hundred large homes outside of Lāhainā, draw their water from three private utility systems that he controls, siphoning underground aquifers and mountain streams to fill swimming pools and irrigate lawns. More than half of all water used in the Launiupoko subdivision, or around 1.5 million gallons a day, goes toward cosmetic landscaping on lawns, according to state estimates. Just over a quarter is used for drinking and cooking.
The scale of this water usage is stunning: According to state data, Launiupoko Irrigation Company and Launiupoko Water Company deliver a combined average of 5,750 gallons of water daily to each residential customer in Launiupoko, or almost 20 times as much as the average American home. The development has just a few hundred residents, but it uses almost half as much water as the public water system in Lāhainā, which serves 18,000 customers.
Martin says he didn’t set out to make Launiupoko a luxury development, but that its value spiked after Maui County imposed rules that limited large-scale residential development on agricultural land. Martin’s development was grandfathered in under those restrictions, and demand for large homes drove up prices in the area. He says criticism of swimming pools and landscaped driveways is rooted in envy.
“People come over and make their land beautiful by using water,” he said.
Martin also maintains that there’s more than enough water for everyone, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Annual precipitation around Lāhainā declined by about 10 percent between 1990 and 2009, drying out the streams near Launiupoko, and now Martin sometimes can’t provide water to all his customers during dry periods. The underground aquifer in the area is also oversubscribed, according to state data, with Martin’s companies and other users pumping out 10 percent more groundwater than flows in each year on average. Climate change could exacerbate this shortage by worsening droughts along Maui’s coast: Projections from 2014 show that annual rainfall could decline by around 15 percent over the coming century under even a moderate scenario for global warming.
In response, the state water commission has intervened to stop Martin and other developers from overtapping West Maui’s water, setting strict limits on water diversion and fining his companies for violating those rules. Last year, the state took full control of the region’s water, potentially jeopardizing the future of Martin’s luxury subdivisions and making it harder for him to build more in the area.
Now, though, Martin is poised to play a key role as West Maui recovers from the Lāhainā wildfire, which destroyed 2,200 structures, including six housing units Martin had developed. Nine of his employees lost their homes. As of early November, more than 6,800 displaced people on Maui remained in hotels or other temporary lodging. Millions of dollars in federal funds are expected to flow into the state for reconstruction. Martin, with his dozens of development companies and thousands of acres of vacant land, is perfectly positioned to build new homes. And his concerns about water regulations slowing development may find a more sympathetic audience as local officials seek to address a post-fire housing crisis.
Moreover, he is itching to build. Before the fire, county and state officials were shooting down most of his new building proposals amid a concern about overdevelopment, even the ones that Martin pitched as affordable workforce housing. Martin thinks he can mitigate West Maui’s fire risk and its housing crisis by getting rid of the barriers that prevent developers like himself from building more houses with irrigated farms and green lawns.
“What I just want is the water to be able to be used on the land, which God intended it to,” he said.
Martin Controls the Water
Daniel Kuʻuleialoha Palakiko doesn’t know what deity Martin is referring to.
“Ke Akua is a God of love and restoration and abundant life,” he told the water commission during September’s hearing, using the Hawaiian word for God. Palakiko had flown to Honolulu with many other Maui residents to urge the state officials to uphold their responsibility to protect water.
Palakiko doesn’t take his land, or water, for granted. He was a teenager in Lāhainā in the 1980s when his family started getting priced out by rising rents. That’s when his dad remembered that his own father had once shown him the family’s ancestral land in nearby Kauʻula Valley. According to Palakiko’s grandfather, the family had been forced out by the Pioneer Mill sugar plantation, which had diverted the Palakikos’ water to irrigate crops. Palakiko’s family still owned the title to the land, and his father was determined to find a way to reclaim it.
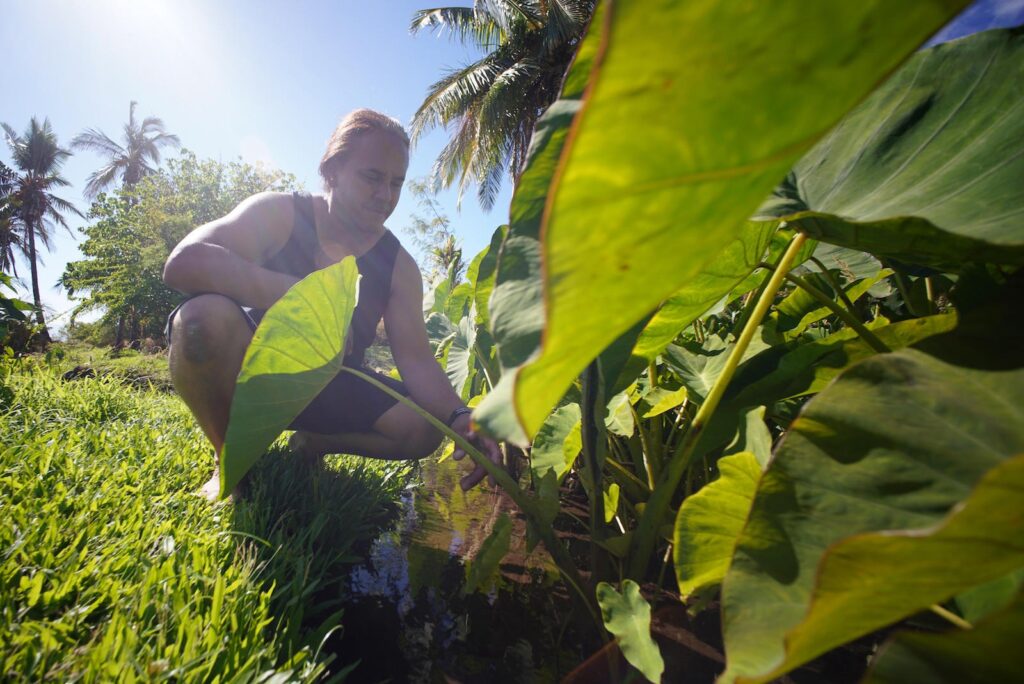

First they cleared brush by cutting firebreaks and burning the overgrowth, controlling the flames with five-gallon buckets of water hauled from a nearby river. Once they had opened enough land to build a house, the Palakikos worked out a deal with Pioneer Mill to restore free water access to their property, connecting their home to the plantation’s water system with a series of 1½-inch plastic pipes.
Access to that water meant that the Palakikos could live on their ancestral land for the first time in generations. Back then, Palakiko says, their property felt isolated from Lāhainā, accessible only by old cane field roads that could take 45 minutes to reach town. But the family didn’t mind. It was enough to be able to stay on Maui when so many other Native Hawaiians were forced by economic necessity to leave.
That isolation didn’t last. In 1999, Pioneer Mill harvested its last sugar crop, ending 138 years of cultivation in Lāhainā. The abandoned fields turned brown and Palakiko heard that the company was selling off thousands of acres. Where once the Palakikos had seen Filipino plantation workers tending to crops, they noticed fair-skinned strangers and surveyors exploring the fallow grounds.
The Palakikos soon realized that the land was now in the hands of Peter Martin, who had joined other local investors to buy everything he could of the old plantation land. These new owners soon subdivided the land and sold parcels at ever higher prices as demand for the area known as Launiupoko kept increasing. It didn’t matter that the area was zoned for agriculture: Like many other developers, Martin took advantage of a legal provision that allowed homeowners to build luxurious estates on such land as long as they did some token farming of crops like fruit or flowers, no matter how perfunctory it might be.
By the time Martin finished the development, which included around 400 homes on around 1,000 acres, he was diverting almost 4 million gallons from the stream every day, according to state data, almost as much as the 4.8 million gallons Pioneer Mill had diverted each day before it shut down.
Some days the Palakiko family would wake up to find no water running through the pipes. By the afternoon, puddles along the stream would evaporate and fish would flop on the hot rocks, suffocating. It wasn’t just the Palakikos who were suffering, but the whole river system: As Martin diverted water from the mountains, the waterway dried up farther downstream, threatening the native fish and shrimp that lived in it. Palakiko appealed to Martin’s new water utility, Launiupoko Irrigation Company, but he said the company was hostile. First it tried to shut off the water the family had been receiving through plastic pipes, then asked the family to pay for water they’d always drawn for free, only relenting after the Palakikos fought back.
In addition to diverting water away from Native Hawaiian families, Martin has tried to force some from their land. In 2002, his Makila Land Company filed a so-called “quiet title” case against the Kapus, another farming family whose land borders the Palakikos, seeking to claim a portion of the family’s ancestral land as its own. This legal strategy, which allows landowners to take control of properties that may have multiple ownership claims, later gained notoriety when Mark Zuckerberg used it to consolidate his holdings on Kauai.
When the Kapus fought back, the company kept them in court for almost two decades, appealing over and over to gain the rights to a 3.4-acre parcel. The situation between Martin and the Kapu family became so tense that in 2020, Martin sought a restraining order against one member of the family, Keeaumoku Kapu, accusing him of “verbally attack[ing] me with an expletive-laced tirade” and blocking Martin’s access to the disputed land. The court imposed a mutual injunction against Martin and Kapu later that year; two years later, Kapu finally prevailed in court and secured the title to his property.
Keep Environmental Journalism Alive
ICN provides award-winning climate coverage free of charge and advertising. We rely on donations from readers like you to keep going.
Donate NowMartin’s companies filed multiple quiet-title lawsuits over the years as Martin sought to consolidate control of the land around Launiupoko. Just after it began litigation against the Kapus, Makila Land Company made a similar claim against a neighboring taro farmer named John Aquino, seeking to seize a portion of the land belonging to Aquino’s family. The company won the slice of land in an appellate court in 2013, but the Aquino family stayed put. Police arrested Aquino in 2020 after two of Martin’s employees drove a semi onto the land; Aquino had smashed the truck’s windows with a baseball bat. Makila later filed a trespassing lawsuit in 2021 against Brandon and Tiara Ueki, who also live near the Kapus. The parties agreed to dismiss the case the following year after an apparent settlement. More recently, Martin has fanned even more frustration by selling properties with contested titles, prompting at least one ongoing legal battle.
Meanwhile, Martin and his fellow investors sought to expand to other parts of West Maui with several large-scale developments in areas along the coastline. In one instance, he and another pair of developers named Bill Frampton and Dave Ward proposed building 1,500 homes, including both single and multifamily housing units, in the small beachfront town of Olowalu, even though water access in the area is minimal and rainfall is declining. The developers later scrapped the project following protests from environmental activists, but in the meantime, Martin sold off a few dozen more lots in Olowalu, where he has a home. He also created another utility, Olowalu Water Company, to supply homes in the area with stream water.
Hawaiʻi, like most of the Western United States, allocates water using a “rights” system: A person or company can own the right to draw from a given water source, often on land they own, but they can’t own the water source itself. In states like Oregon and Arizona, this system has led to conflicts between settlers and tribal nations, but in Hawaiʻi the law provides explicit protection for Native Hawaiian users. State law stipulates that traditional and cultural uses, such as taro farming, “shall not be abridged or denied.” In times of shortage, Native users have the highest priority.
In 2018, the state water commission imposed so-called “flow standards” on several West Maui streams, capping the amount of water that Launiupoko Irrigation Company and Olowalu Water Company could divert at any given time. Palakiko had mixed feelings about this: He didn’t want to cede more control over the water that his family had used for generations, but it felt necessary in order to ensure someone could hold the companies accountable.
Even after these rules took effect, though, Martin’s water utility companies violated them dozens of times. When the state threatened to fine the companies, Launiupoko Irrigation Company stopped taking water from its stream completely. Residents of the lush Launiupoko subdivision soon had to ration irrigation water, and the Palakikos lost their access altogether. Their pipes stayed dry for more than a week until a judge ordered Martin’s company to turn on the tap back on.
As the state cracked down on stream diversions, Martin sought to secure more water by tapping an aquifer beneath Lāhainā. Here again, he was accused of infringing on Native Hawaian cultural resources: When his West Maui Construction Company started digging a ditch for a water line in 2020, it excavated an area that contained Native Hawaiian burial remains, triggering protests. Five Native Hawaiian women activists climbed into the company’s ditch to stop the construction project and were arrested. A judge later found the company broke the law by starting construction on the water line without all the requisite permits.
The new restrictions started to hamper Martin’s development activities. Last year, his Launiupoko Water Company applied to the state’s utility regulator for permission to deliver water to a new area near Lāhainā. The company said it had agreed to supply a nearby landowner with potable water for 11 new homes, and told the state it needed to increase its groundwater pumping by at least 65,000 gallons per day. The regulator rejected the expansion plan, saying the company had omitted “basic information” about where it would get this new water. The landowner that would have received the water was another company in which Martin has an ownership stake.
Even as his companies’ plans faced headwinds, Martin continued to benefit. He loaned Launiupoko Irrigation Company a total of $9 million in recent years as the company tried to expand its Lāhainā well system, charging 8 percent interest. The company tried in 2021 to secure a bank loan for the project, but three banks turned it down, with one noting that the company’s “interest payments to Pete” were “substantial.”
Glenn Tremble, a top executive at West Maui Land Company, the company at the center of Martin’s development empire, said in response to a list of questions that Grist’s statements were “generally false and often libelous.” Tremble noted that Martin has built affordable housing units on West Maui and donated to churches. He said that Martin is “well positioned to assist with recovery and efforts to rebuild.”
If Martin’s track record with water and land made him infamous in Lāhainā, it also invigorated local support for even stricter water controls. Palakiko’s long campaign for more attention to the region’s water problems finally bore fruit last year when the state designated West Maui as a “water management area.” Instead of just setting limits on how much water Martin’s companies could take from West Maui streams at any given time, the state water commission announced that it would revamp the area’s entire water system, giving highest priority to Indigenous cultural uses like taro farming. That may mean limiting access for Martin’s luxury developments, though Tremble disputes this.
“We’ve heard a lot from the community about the development of West Maui Land’s holdings in Launiupoko,” said Dean Uyeno, the interim chair of the state water commission, about the decision. “To continue building in these types of ways is going to keep taxing the resource.” The question, Uyeno said, is whether developers “can … find a way to [be] building more responsible development that balances the resources we have.”
Martin thinks the argument that water is a scarce resource is a “red herring.” He argues that the market is calling for more housing, not more water for native fish that rely on the streams.
“All the people [who] ever come to me say, ‘Peter, can you get me a house? I want a place to live,’” he said. “They don’t go, ‘Oh, I wish I had [shrimp] for dinner.’ That’s not what people tell me. They say, ‘Can’t you give me some house, some land?’ I go, ‘I’d love to but the government won’t let me.’”
The Water Needed to Fight Fires
In the days before the wildfire, Martin’s executives worked long hours in his West Maui Land Company office filling out 30 state applications justifying their current water usage and seeking more, in accordance with the state’s revamp of the area’s water system. They submitted the applications just days before the state’s August 7 deadline. The day after the deadline, Lāhainā burned.
To Martin, this is not a coincidence. He believes the state water commission’s efforts to more strictly regulate water enabled the fire by preventing more construction of homes with irrigated lawns — in other words, more development would have made West Maui more resilient to fire. The day before the water commissioners met in September, he wondered if the commissioners would acknowledge their responsibility for the wildfire deaths and regretted not pushing harder against their restrictions.
“I feel I actually have blood on my hands because I didn’t fight hard enough,” he said.
There’s no evidence that the state management rules, which are still in the process of going into effect, had any bearing on the fire. When Grist relayed this argument to the interim leader of the state’s water commission, he was stunned.
“That actually leaves me speechless,” said Uyeno. “I don’t know how to respond to that.”
Palakiko and his family spent the day of the fire watching the smoke rising from the coastline, watering the grass on their property and praying the winds wouldn’t shift, sending the flames their way. Five years earlier, another fire fueled by a passing hurricane had burned down two homes on their land.
That day, their prayers were answered. But when Palakiko’s son, a firefighter, came home shaken from his shift fighting the blaze, the family realized that the West Maui they had known their whole lives was gone.
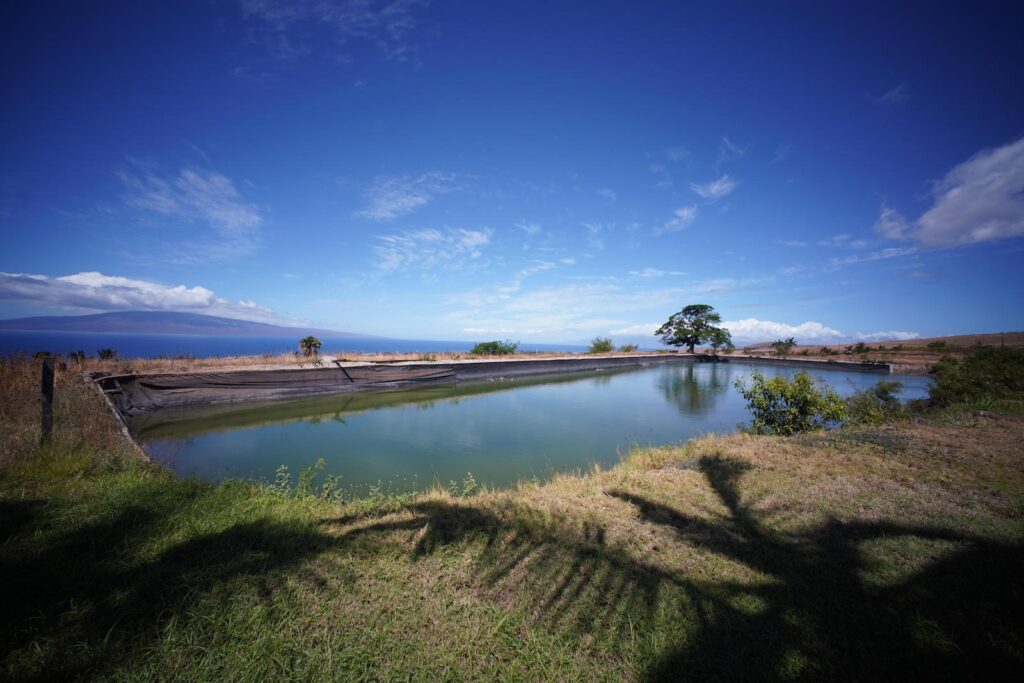

Two days later, Palakiko received another shock when he read Tremble’s letter accusing Kaleo Manuel, the deputy director of the water commission, of delaying the release of firefighting water. The letter argued that Manuel had waited to release water to West Maui Land Company’s reservoir until he had checked with the owners of a downstream taro farm. That farm belongs to the Palakikos.
The company’s allegations were explosive. The state attorney general launched an investigation and requested that the commission reassign Manuel, who had been instrumental in establishing the Lāhainā water management area and was the only Native Hawaiian to ever hold that position. Governor Josh Green temporarily suspended the rules that limit how much water Martin’s companies and other water users can draw from West Maui streams. The state later reinstated Manuel and restored the rules. In a statement to Grist, Tremble said he respects Manuel’s “commitment and his integrity” and said that “the problem is the process, or lack thereof, to provide water to Maui Fire Department and to the community.”
While there was no evidence that filling the reservoir would have stopped the fire from destroying Lāhainā, and firefighting helicopters wouldn’t have been able to access the reservoir due to high winds on the day in question, there’s a growing consensus among scientists in Hawaiʻi that one factor in its rapid spread was the proliferation of nonnative grasses on former plantation lands — including lands that Peter Martin owns.
Before the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom in 1893, before the dominance of the sugar industry allowed plantations to divert West Maui’s streams, Hawaiian royalty lived on a sandbar in the midst of a large fishpond within a 14-acre wetland in Lāhainā, which was known as the Venice of the Pacific.
After plantation owners diverted streams for their crops, the royal fishpond became a stagnant marsh, and later was filled with coral rubble and paved over. Now, Palakiko imagines what it would be like if the streams were allowed to resume their original paths: what trees would grow, what native grass could flourish, what fires might be stopped. He doesn’t think this vision is at odds with the need to address Maui’s housing crisis.
For Palakiko, the fight over the future of water in Lāhainā is about more than just who controls the streams in this section of Maui. It’s also in some ways a referendum on what future Hawaiʻi will choose: one that reflects the worldview of people like Palakiko, who see water as a sacred resource to be preserved, or that of people like Martin, who sees it as a tool to be used for profit.
To Martin, such a shift is unsettling.
“I mean, for a hundred years, you could take all the water, and all of a sudden these guys come in, and say, ‘Oh, you can’t take any water,’” Martin said. “And they made it sound like I’m this terrible person.”
Grist is a nonprofit, independent media organization dedicated to telling stories of climate solutions and a just future. Learn more at Grist.org